Commercial aviation companies in Canada and their crew follow many laws and regulations. One of these are the Canadian Aviation Regulations 705, which specifically applies to airline operators. These are in place to ensure the safety of these operators and the public, given that civil aviation is a large factor affecting the lives of people and activities of many businesses.
What is Canadian Aviation Regulations 705?
The Canadian Aviation Regulations 705 is a subpart of the Canadian Aviation Regulations (CARs). The CARs are one of the regulations enacted to implement the provisions of the federal Aeronautics Act, along with the Commercial Air Service Standards (CASS). In turn, the Act is the umbrella law that regulates civil aviation in the country.
These laws and regulations are important considerations not just for airline operators, but also for their staff, crew, and customers. These cover the following:
- registration and licensing process of operators and their crew
- guidelines to ensure the safety of their customers
- military investigations for accidents involving the military and civilians
- administrative procedures granted to Transport Canada
- offences when it comes to civil aviation and their penalties
#Canada 🇨🇦’s civil aviation medical examiners assess #pilots regularly to ensure they meet the fitness requirements to fly! For more info: https://t.co/Bx8KTpq9dF pic.twitter.com/pylqiYX4sX
— Transport Canada (@Transport_gc) July 20, 2018
Read further for more information on how the CARs regulate pilots. If you’re a pilot or an aircraft operator in Calgary or Edmonton, reach out to one of the Lexpert-ranked best aviation lawyers in Alberta.
Obligations under the Canadian Aviation Regulations 705
The Canadian Aviation Regulations 705 (CARs 705) governs airline operations. It covers operations, certifications of crew, and setting up of safety guidelines. It has 12 Divisions:
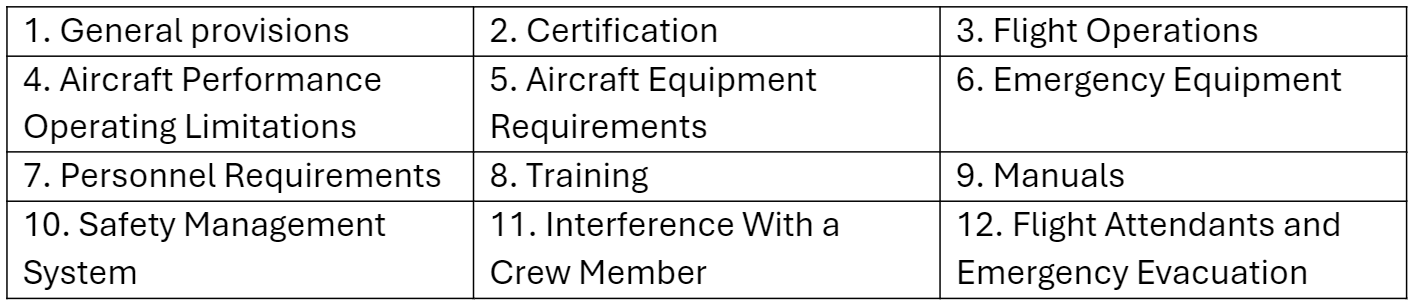
Application of the Canadian Aviation Regulations 705
Just like the other Subparts of the CARs, the CARs 705 only applies to a specific operator or aircraft. Division I says that CARs 705 apply to Canadian air operators that operate:
- in an air transport service; or
- in aerial work involving sightseeing operations
The type of aircraft covered by CARs 705 are the following:
- airplane:
- that has a MCTOW of more than 8,618 kg (19,000 pounds); or
- for which a Canadian type certificate has been issued authorizing the transport of 20 or more passengers; but
- does not include airplane designated as a commuter operator under CARs 704
- helicopter: has a seating configuration, excluding pilot seats, of 20 or more
- other aircraft: authorized by the Minister of Transport to operate under CARs 705
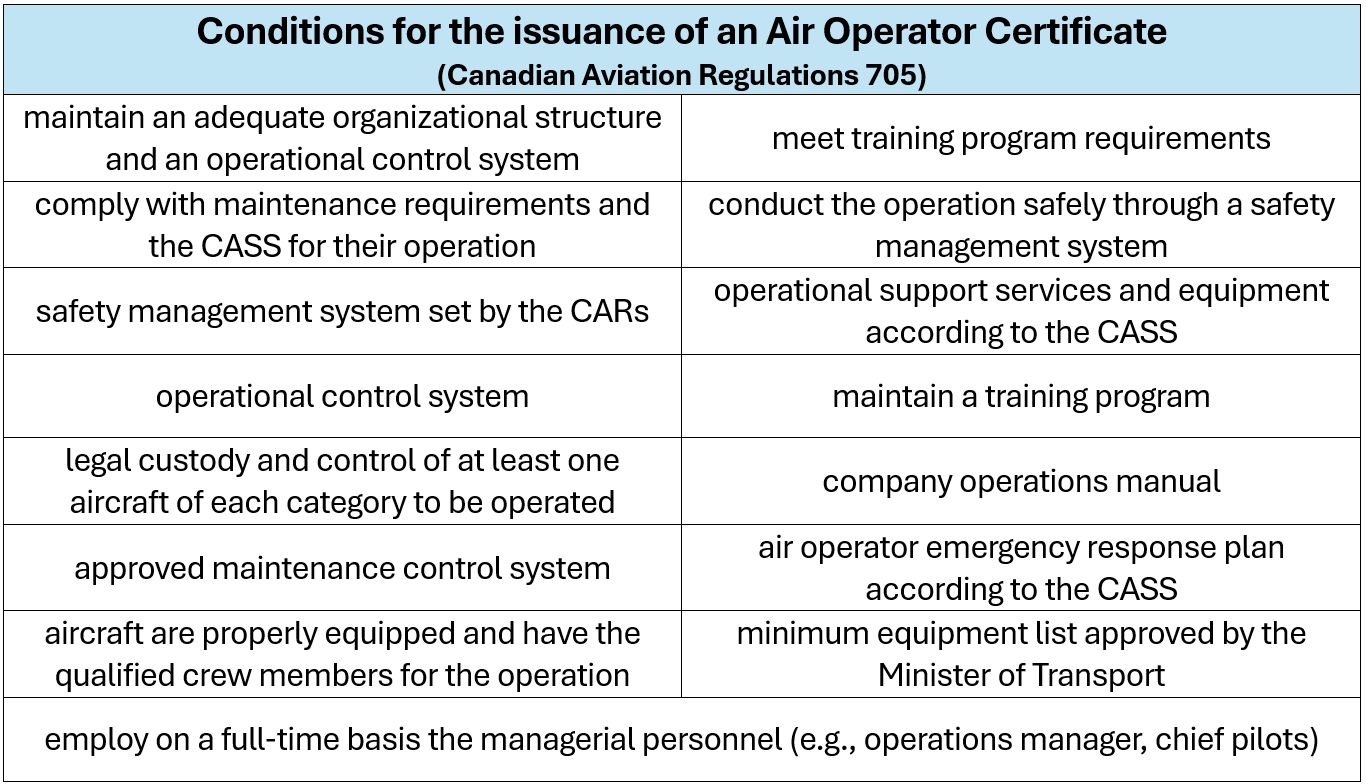
Certification of airline operators
CARs 705 provides for various requirements that air operators must follow before, during, and after their work. They must have an air operator certificate which allows them to run a commercial air service. It is issued by Transport Canada, only if air operators can fulfill the following:
Who are the 705 operators in Canada?
705 operators are the airline operators covered by the Canadian Aviation Regulations 705 (hence, the 705 designation). Whether they’re one of the major commercial airlines in Canada, or the smaller airlines, all are named as 705 operators. They’re governed by the CARs 705, other related subparts of the CARs, and other laws in Canada related to aviation.
Flight operations of 705 operators
The CARs 705 govern the flight operations of 705 operators, which cover rules for the operators’ personnel and the aircraft itself.
705 operators must comply with these guidelines:
- operating instructions: all personnel must be informed of their duties and must follow the procedures specified in their company operations manual
- aircraft maintenance: all aircraft must be maintained according to their maintenance control system
- admission of inspectors: Transport Canada’s air carrier inspectors and cabin safety inspectors must be admitted for the performance of their appropriate roles
- safety procedures: operator must have the safety procedures for the safety of their passengers which also meet the CASS
- emergency equipment: operator must have equipment listed by the CARs and the CASS (e.g., megaphones, first aid kits, emergency medical kit, etc.)
What is needed to be a chief pilot in Canada?
The qualification of a chief pilot is listed under CARs 705 and the CASS. It says that a chief pilot must:
- hold a valid:
- Airline Transport Pilot Licence (airplanes);
- Instrument Rating for the group of airplanes; and
- type rating for at least one of the types of airplanes operated
- have experience as a pilot-in-command for at least 3 years with the appropriate aircraft; commercial operations experience is not required
- be qualified for line flying on one of the types of airplanes operated
- know the company operations manual, training manuals, standard operating procedures, the CARs, and the CASS
- not be convicted of:
- any offence under the Aeronautics Act
- two or more convictions under the CARs involving separate unrelated events
Personnel requirements under Canadian Aviation Regulations 705
Aside from the qualification of a chief pilot, the CARs 705 also provides for the qualification of the other personnel and crew of a 705 operator, such as:
- pilot-in-command, second-in-command or cruise relief pilot
- flight engineer or a second officer
- flight attendant
- flight dispatcher
These crew and personnel must meet the training requirements under the CARs and/or the CASS, and must be a holder of the certification according to their role. These are also subject to specific validity periods, so these crew and personnel must renew their certifications and training before expiry.
For more information about the Canadian Aviation Regulations 705, consult a one of the best aviation lawyers in Canada as ranked by Lexpert.





